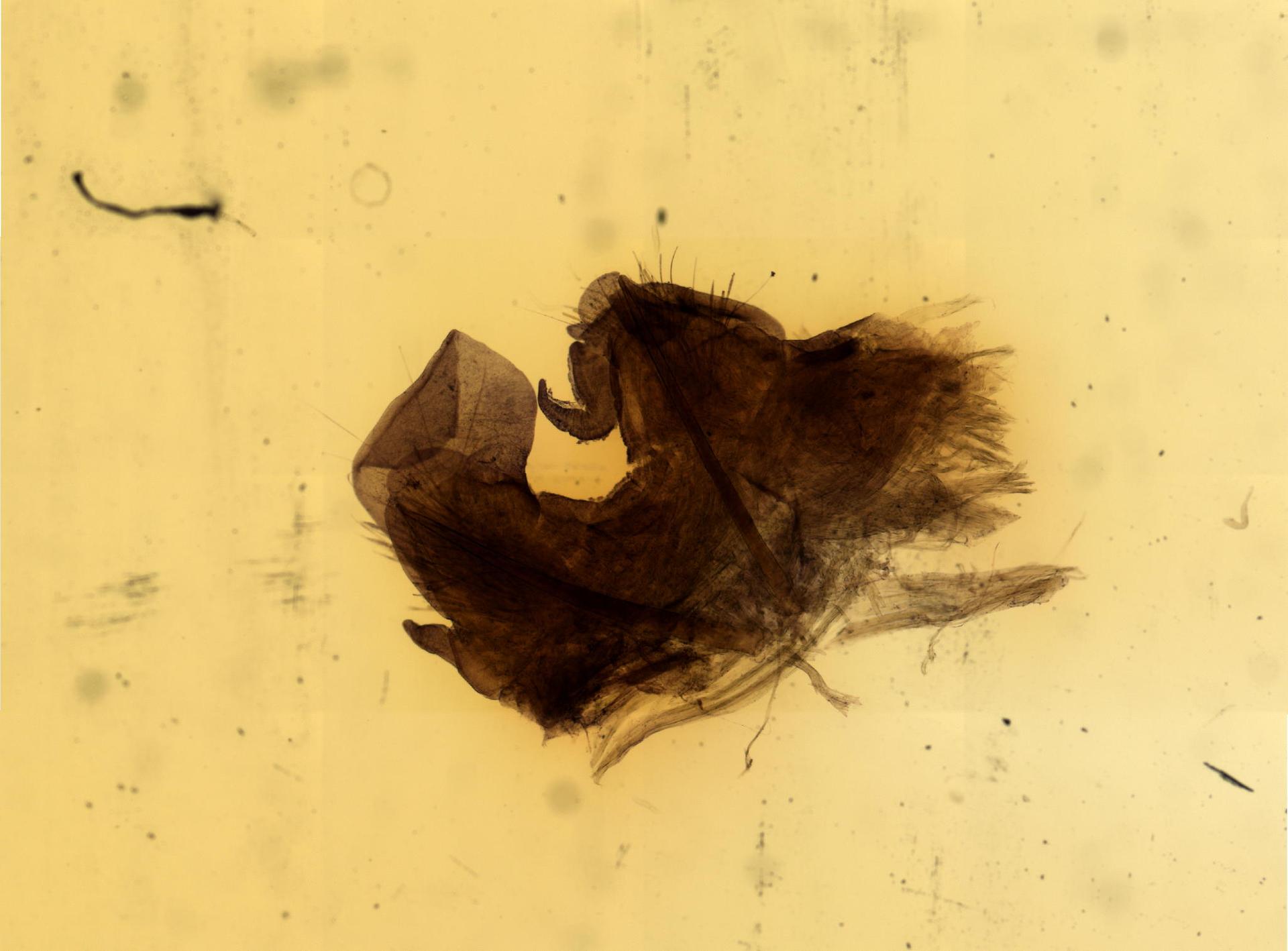
Scheldt species taxon details
Nephtys Cuvier, 1817
129370 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:129370)
accepted
Genus
- Species Nephtys caeca (Fabricius, 1780)
- Species Nephtys cirrosa Ehlers, 1868
- Species Nephtys hombergii Savigny in Lamarck, 1818
- Species Nephtys longosetosa Örsted, 1842
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
recent only
Cuvier, Georges L., 1817. Le règne animal distribué d'après son organisation : pour servir de base a l'histoire naturelle des animaux et d'introduction a l'anatomie comparée. VOLUME 4. Les Zoophytes, les Tables, et les Planches. Deterville, Paris., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/17709
page(s): Additions & Corrections p.173 [details]
page(s): Additions & Corrections p.173 [details]
Read, G.; Fauchald, K. (Ed.) (2025). World Polychaeta Database. Nephtys Cuvier, 1817. Accessed through: VLIZ Consortium Scheldt Species Register at: https://www.scheldemonitor.nl/speciesregister/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=129370 on 2025-09-11
VLIZ Consortium. Scheldt Species Register. Nephtys Cuvier, 1817. Accessed at: https://scheldemonitor.be/speciesregister/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=129370 on 2025-09-11
Date
action
by
original description
Cuvier, Georges L., 1817. Le règne animal distribué d'après son organisation : pour servir de base a l'histoire naturelle des animaux et d'introduction a l'anatomie comparée. VOLUME 4. Les Zoophytes, les Tables, et les Planches. Deterville, Paris., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/17709
page(s): Additions & Corrections p.173 [details]
additional source Glasby, Christopher J.; Read, Geoffrey B.; Lee, Kenneth E.; Blakemore, R.J.; Fraser, P.M.; Pinder, A.M.; Erséus, C.; Moser, W.E.; Burreson, E.M.; Govedich, F.R.; Davies, R.W.; Dawson, E.W. (2009). Phylum Annelida: bristleworms, earthworms, leeches. <em>[Book chapter].</em> Chapt 17, pp. 312-358. in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2009). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 1. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia. Canterbury University Press, Christchurch. [details] Available for editors
additional source Fauchald, K. (1977). The polychaete worms, definitions and keys to the orders, families and genera. <em>Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County: Los Angeles, CA (USA), Science Series.</em> 28:1-188., available online at http://www.vliz.be/imisdocs/publications/123110.pdf [details]
additional source Bellan, G. (2001). Polychaeta, <i>in</i>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. <em>Collection Patrimoines Naturels.</em> 50: 214-231. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Day, J. H. (1967). [Errantia] A monograph on the Polychaeta of Southern Africa. Part 1. Errantia. British Museum (Natural History), London. pp. vi, 1–458, xxix., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/8596 [details]
identification resource Dixon-Bridges, Kylie; Gladstone, William; Hutchings, Patricia A. (2014). One new species of <em>Micronephthys</em> Friedrich, 1939 and one new species of <em>Nephtys</em> Cuvier, 1817 (Polychaeta: Phyllodocida: Nephtyidae) from eastern Australia with notes on <em>Aglaophamus</em> <em>australiensis</em> (Fauchald, 1965) and a key to all Australian species. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 3872(5): 513-540., available online at https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3872.5.5
page(s): 531 [tabulation of Australian and Indo-pacific species of Nephtys]] [details] Available for editors
identification resource Hossain, M. Belal; Hutchings, Pat. (2016). <em>Nephtys bangladeshi</em> n. sp., a new species of Nephtyidae (Annelida: Phyllodocida) from Bangladesh coastal waters. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 4079(1): 41-52., available online at http://biotaxa.org/Zootaxa/article/view/zootaxa.4079.1.3
page(s): 48; note: Table of Indo-Pacific Nephtys species [details]
page(s): Additions & Corrections p.173 [details]
additional source Glasby, Christopher J.; Read, Geoffrey B.; Lee, Kenneth E.; Blakemore, R.J.; Fraser, P.M.; Pinder, A.M.; Erséus, C.; Moser, W.E.; Burreson, E.M.; Govedich, F.R.; Davies, R.W.; Dawson, E.W. (2009). Phylum Annelida: bristleworms, earthworms, leeches. <em>[Book chapter].</em> Chapt 17, pp. 312-358. in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2009). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 1. Kingdom Animalia: Radiata, Lophotrochozoa, Deuterostomia. Canterbury University Press, Christchurch. [details] Available for editors
additional source Fauchald, K. (1977). The polychaete worms, definitions and keys to the orders, families and genera. <em>Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County: Los Angeles, CA (USA), Science Series.</em> 28:1-188., available online at http://www.vliz.be/imisdocs/publications/123110.pdf [details]
additional source Bellan, G. (2001). Polychaeta, <i>in</i>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. <em>Collection Patrimoines Naturels.</em> 50: 214-231. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Day, J. H. (1967). [Errantia] A monograph on the Polychaeta of Southern Africa. Part 1. Errantia. British Museum (Natural History), London. pp. vi, 1–458, xxix., available online at http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/8596 [details]
identification resource Dixon-Bridges, Kylie; Gladstone, William; Hutchings, Patricia A. (2014). One new species of <em>Micronephthys</em> Friedrich, 1939 and one new species of <em>Nephtys</em> Cuvier, 1817 (Polychaeta: Phyllodocida: Nephtyidae) from eastern Australia with notes on <em>Aglaophamus</em> <em>australiensis</em> (Fauchald, 1965) and a key to all Australian species. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 3872(5): 513-540., available online at https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3872.5.5
page(s): 531 [tabulation of Australian and Indo-pacific species of Nephtys]] [details] Available for editors
identification resource Hossain, M. Belal; Hutchings, Pat. (2016). <em>Nephtys bangladeshi</em> n. sp., a new species of Nephtyidae (Annelida: Phyllodocida) from Bangladesh coastal waters. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 4079(1): 41-52., available online at http://biotaxa.org/Zootaxa/article/view/zootaxa.4079.1.3
page(s): 48; note: Table of Indo-Pacific Nephtys species [details]
 Present
Present  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
| Language | Name | |
|---|---|---|
| English | shimmy wormscatworms | [details] |